Cable Q & A with Greg Knowles! How to select the correct cable for your application.
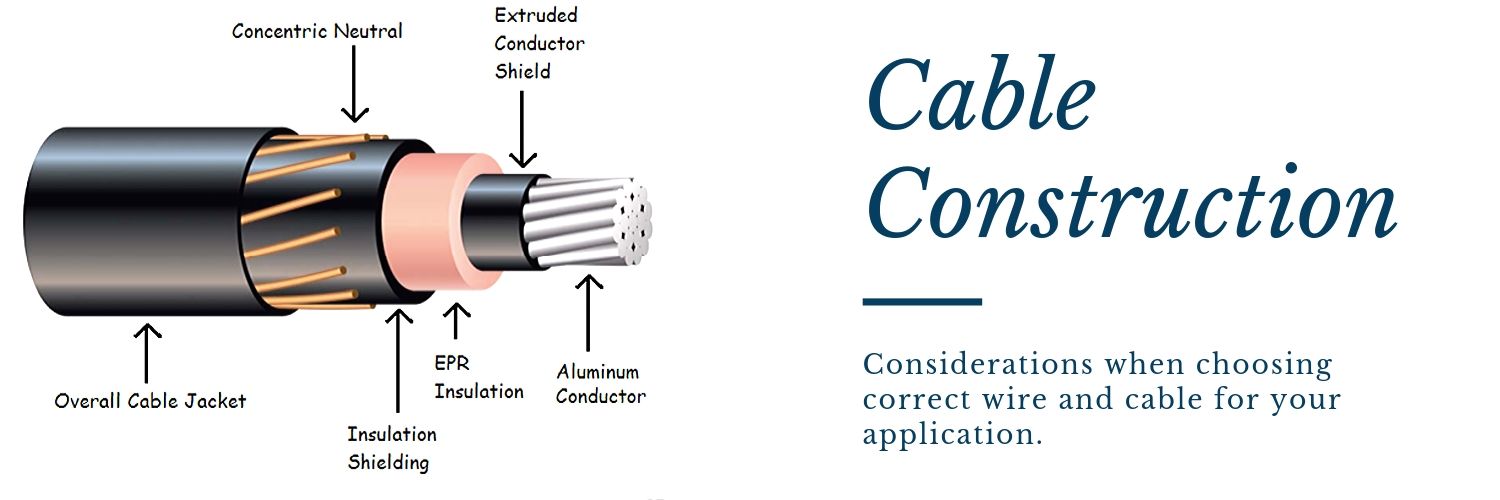
Choosing the right cable can be tricky, given all the different variables involved. This Q&A blog is intended to answer some of the most common questions which will help you choose the correct cable for your application. Before we go through the list, let’s go over some of the wire and cable basics. The best way to look at cable construction is from the inside out, with the inside being the conductor, and the outside being the jacket. In between the conductor and the jacket, can – but doesn’t always include, the insulation, shielding, separators and signal carriers.
The picture above is a perfect example of cable construction.
Now, let’s answer some of the most common questions.
Q: What does the voltage rating of a cable mean?
A: The voltage rating is the maximum voltage that the jacket and insulation can insulate against. It is a maximum rating, meaning voltages lower than the rating are ok, but never higher.
Q: What might happen if we exceed the amperage rating?
A: Exceeding the amperage rating of cable can, and usually does, cause the cable to heat up and may catch fire. Cable conductors are designed to offer low resistance up to a certain amperage, and when the rating is exceeding, resistance increases rapidly causing the conductors to heat up. A good rule of thumb is to rate your cable 20% above the maximum amperage available.
- What is the difference between amperage rating and temperature rating.
- The temperature rating is the ambient temperature (air temperature) that the cable can handle while maintaining its electrical and insulating properties. Cable is rated for maximum heat and cold. For example, extra flexible cables for mines and generators are typically rated between -40 deg C (or F) and 105 deg C.
- What termination options are available for different cables.
- The termination options depend of the type of conductor, application and what the cable is connecting to. There are far too many options to discuss here, so it is best to consult your application with your distributor sales person and they can help.
Q: What determines the rated use of the cable?
A: The rated use determines the type of environment a cable can be used in. For example, certain types of mining cable is rated to be dragged behind shovels or hung from CAB cable hangars down a mine shaft. Other cables are rated to be buried directly in the ground. The rated use is commonly found in the cable specifications.
- How do I know how many conductors are in a cable:
A: Cable specifications typically begin with the conductor size first, then the conductor count. For example, a portable power cable that contains 4 - 4/0 conductors would be described as 4/0-4C. With 4/0 being the cable size and 4C being 4 conductors. The number of conductors a cable can have is almost unlimited. Some telecommunication cables can have over 100 conductors, while temporary power cable generally have only one.
- What do the different colors of cable jackets mean?
- Cable jackets, which is the last layer of a cable, can come in a variety of colors. The significance varies depending on the application, however it rarely has to do with specifications or ratings. The most common uses are for a company to identify which cable is theirs, visibility in outdoor environments, or to designate a specific phase the cable is connected to. For example, Caterpillar might want their cable in all yellow, and a mine that has cable laying near a road would want it bright red.
If you would like help in selecting the correct wire and cable for your application, contact one of our knowledgeable sales people at info@atielectrical.com or call 1-800-597-9377. You can also find specifications for many of the most common cable types on our website at www.atielectrical.com.

 CALL OR TEXT NOW 800-597-9311
CALL OR TEXT NOW 800-597-9311
Leave a comment